FISHTERM bilingual dictionary Search results for 'Trawler' (2 record(s))
| RECORD No. | 168 |
| AUTHOR | ELAD D. F. |
| DATE OF CREATION | |
| LAST UPDATE | 2023-01-28 00:00:00 |
| ENGLISH | |||||
| SUBJECT FIELD |
| ||||
| TERM | * Fishing trawler statut: préféré ; * trawler (noun) statut: admis | ||||
| PART OF SPEECH | noun | ||||
| PLURAL | Fishing trawlers ; Trawlers ; | ||||
| ETYMOLOGY | First Known Use 1629. From trawl and -er; from Dutch tragelen, ‘to trawl’; from Middle Dutch traghelen, ‘to drag’; from Middle Dutch traghel, ‘dragnet’; from Classical Latin tragula, ‘dragnet’ | ||||
| ETYMOLOGY SOURCE |
Antidote bilingual 10 v2.1 (2019). | ||||
| DEFINITION |
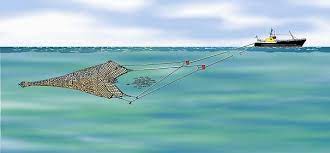
a commercial fishing vessel designed to operate fishing trawls. They are often a type of powerboat, designed for long-distance cruising, and drag funnel-shaped trawl nets through the water to catch fish or shellfish. | ||||
| DEFINITION SOURCE | Fishterm | ||||
| RECORD No. | 223 |
| AUTHOR | ELAD D. F. |
| DATE OF CREATION | |
| LAST UPDATE | 2023-01-28 00:00:00 |
| FRENCH | |||||||||||||
| SUBJECT FIELD |
| ||||||||||||
| TERM | * Chalutier statut: préféré ; * Chalutière (nom masculin) statut: admis | ||||||||||||
| PART OF SPEECH | nom masculin | ||||||||||||
| ETYMOLOGY | 1866, Hugo, les Travailleurs de la mer; de chalut; De chalut et -ier ; d’une langue d’oïl du nord-ouest chalut, ‘chalut’ | ||||||||||||
| ETYMOLOGY SOURCE |
Grand Robert de la langue française, en 6 volumes version 2.0 (2005). Antidote bilingual 10 v2.1 (2019). | ||||||||||||
| DEFINITION |
Personne qui pêche au chalut. | ||||||||||||
| PLURAL | Chalutiers ; Chalutières ; | ||||||||||||
| DEFINITION SOURCE |
Antidote bilingual 10 v2.1 (2019). Grand Robert de la langue française, en 6 volumes version 2.0 (2005). | ||||||||||||
| USAGE EXAMPLE | Mais elles rentrent souvent bredouilles, depuis que les chalutiers européens ratissent ces eaux poissonneuses. ( Le Monde.fr) | ||||||||||||
| ENGLISH | |||||||||||||
| SUBJECT FIELD |
| ||||||||||||
| TERM | * Trawler statut: préféré | ||||||||||||
| PART OF SPEECH | noun | ||||||||||||
| PLURAL | Trawlers ; | ||||||||||||
| ETYMOLOGY | First Known Use 1629. From trawl and -er; from Dutch tragelen, ‘to trawl’; from Middle Dutch traghelen, ‘to drag’; from Middle Dutch traghel, ‘dragnet’; from Classical Latin tragula, ‘dragnet’ | ||||||||||||
| ETYMOLOGY SOURCE |
Antidote bilingual 10 v2.1 (2019). Mirriam Webster's Dictionary | ||||||||||||
| DEFINITION |
Someone who fishes using a fishing trawler | ||||||||||||
| DEFINITION SOURCE | Fishterm | ||||||||||||
1. Decree No. 95/413 /PM of 20 June 1995 to lay down certain conditions for the application of fisheries regulations., Chapter I, article 3, paragraph 1:
" Within the meaning of Article 110 of the Act, the following are considered, inter alia as fishing vessels: A) For industrial fishing, trawlers ; - shrimp vessels - longliners - trawlers - sardine vessels - tuna boats. B) For small-scale fishing - traditional canoes or similar; - tailenders "
2. Law No. 94/01 of 20 January 1994 to lay down forestry, wildlife and fisheries regulations in Cameroon, Chapter III, article 127:
" The following shall be forbidden : a) the use of trawlers or fishing vessels equipped with trawling gear within a 3 nautical mile zone of the basic line fixed by decree; b) the use, for any type of fishing, of any material likely to obstruct the mesh of nets or having the effect of reducing their selective action, and no accessory equipment may be placed at the interior of fishing nets. Protective devices may be permitted if such devices have a dimension of more than two times that of the authorised mesh and are placed on the upper part of the net and not behind the net; c) the use for fishing of any diving suit equipped with a respiratory device; d) the presence on board a fishing vessel of respiratory equipment such as a diving suit, a harpoon or of a dangerous fishing weapon, except as a safety precaution; e) the use for fishing of explosives, chemicals, poisons or other noxious substances, electrical currents or headlamps, fire-arms, light or automatic traps or any other devices likely to destroy aquatic fauna and the aquatic environment; f) the construction of dams, embankments, large channels or port facilities without the prior approval of fisheries services. g) the pouring or discharging into the aquatic environment of toxic or noxious materials such as industrial, agricultural or domestic waste and pollutants (pesticides, ferti1izers, sediments, detergents); h) the destruction of the environment within a distance of 50 metres along a water course or over a radius of 100 metres around its source; i) the presence on board a fishing vessel of any fishing nets, whose mesh sizes do not conform to prescribed standards and ensure the protection of species; j) the presence on board a fishing vessel of any destructive devices or of substances that are capable of stunning or disabling fish, as well as any other materials and devices capable of reducing or obstructing the meshes of fishing nets; k) the export of any fishing resource without the prior approval of the services in charge of fisheries; l) the introduction into Cameroon of foreign living fishery resources; m) the capture, sale or possession of any protected fishery resources appearing on a list established by fisheries services, n) fishing in closed areas forbidden by fisheries services. "
3. Images related to 'Trawler'