When asked about the differences between inland fishery and marine fishery, most people are likely to say:
“Inland fishery is fishery in freshwater and brackish water whereas marine fishery is fishery in seawater.”
However, there are lots of note-worthy differences that will broaden your understanding of where these two concepts converge and where they diverge. There are several types of fisheries, and there are many differences and similarities between them. If you are reading this, you are certainly willing to know more about their peculiarities.
Characteristics of Inland Fishery
- Inland fishery is rearing fish in freshwaters like streams, canals, ponds, reservoirs, lakes and rivers.
- Most of the fish are cultured or captured for human consumption only in rare cases are excesses processed as inputs or feed for other agricultural sectors.
- Inland fishery water bodies are typically low in salinity – below 33ppt dissolved salts.
- Examples of inland fishery species include freshwater and brackish species like catfish, common carp, kanga, river prawns, etc.
- Inland fishery often englobes subsistence fishery, traditional fishery, artisanal fishery, and recreational fishery, and small-scale fishery.
- Inland fishery is often done on a small scale. This implies lower fishing effort, small capital, and smaller paid labour.
- Gears used in inland fisheries are mostly manual and small. E.g., fishing hooks and lines, pots, castnets, and seins.
- Inland fishery is subdivided into two types: freshwater and brackish water fisheries.
Characteristics of Marine Fishery
- Marine fishery is done in seawater or saltwater. Partly for human consumption while excesses are processed into derived and by-products like fishmeal, fish oil, ash, etc. These marine fish and the products thereof often reach world markets.
- Marine fishes are saltwater species like mackerel, sardines, tuna, rays, oysters, clams, mussels, etc.
- Marine fishery is also known as maritime fishery or saltwater fishery.
- Marine fishery water bodies are typically high in salinity -i.e. above 33ppt dissolved salts.
- Marine fishery is subdivided into two main types: onshore and offshore fisheries.
- Marine fishery uses mostly motorised and large gear. E.g. trawls, motorised boats, dragnets, etc.
- Mostly large-scale, commercial, and industrial.
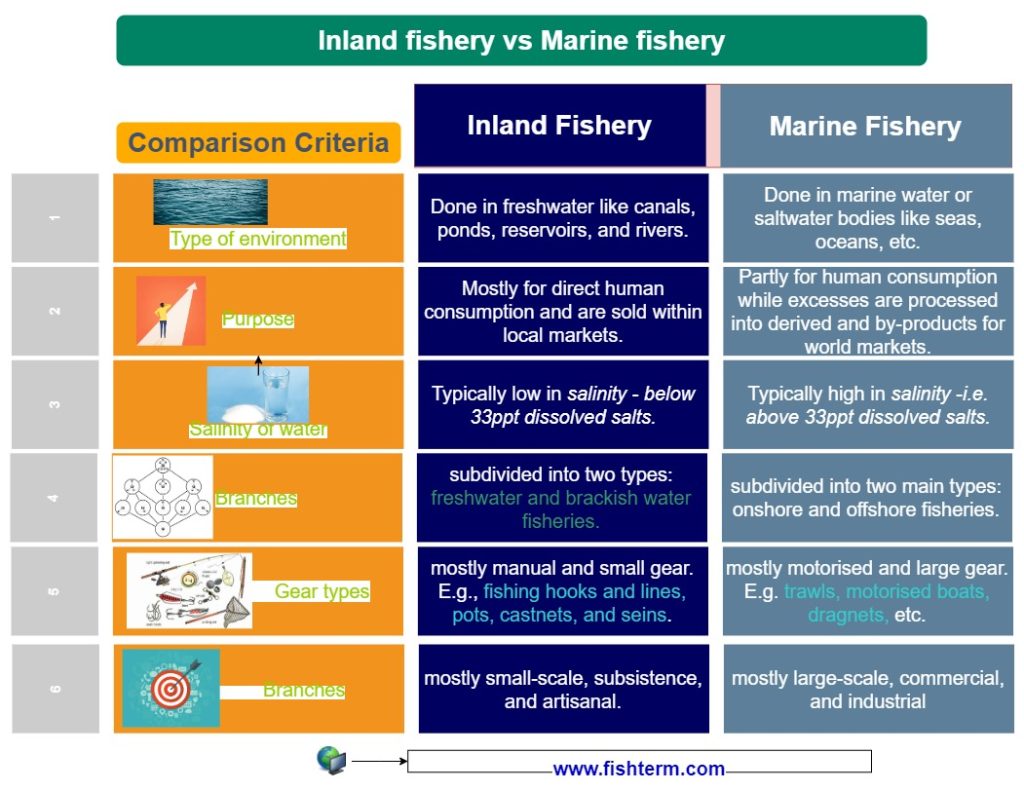
Differences between inland fishery and marine fishery
Let’s look at the key differences between inland fishery and marine fishery in the table below.
| Comparison criteria | Inland fishery | Marine fishery |
| Type of environment | Inland fishery is done in freshwater like canals, ponds, reservoirs, and rivers. | Marine fishery is done in marine water or saltwater bodies like seas, oceans, etc. |
| Purpose | Mostly for direct human consumption and are sold within local markets. | Partly for human consumption while excesses are processed into derived and by-products like fishmeal, fish oil, ash, etc. These marine fish and the products thereof often reach world markets. |
| Example of species concerned | Inland fishes are freshwater and brackish species like catfish, common carp, kanga, river prawns, etc. | Marine fishes are saltwater species like mackerel, sardines, tuna, rays, oysters, clams, mussels, etc. |
| Other appellations | Inland fishery is also known as freshwater fishery. | Marine fishery is also known as Maritime fishery or saltwater fishery. |
| Salinity of water | Inland fishery water bodies are typically low in salinity – below 33ppt dissolved salts. | Marine fishery water bodies are typically high in salinity -i.e. above 33ppt dissolved salts. |
| Branches | Inland fishery is subdivided into two types: freshwater and brackish water fisheries. | Marine fishery is subdivided into two main types: onshore and offshore fisheries. |
| Gear types | Inland fishery uses mostly manual and small gear. E.g., fishing hooks and lines, pots, castnets, and seins. | Marine fishery uses mostly motorised and large gear. E.g. trawls, motorised boats, dragnets, etc. |
| Scale | mostly small-scale, subsistence, and artisanal. | mostly large-scale, commercial, and industrial. |
Conclusion
The differences and similarities between the concepts mentioned above have been elaborated to cover just the basics. Consult related posts made solely on Inland fishery or Marine fishery to obtain more information. Kindly drop more types in the comment section below.
Leave a Reply