Overview of the origin of the 6 major fishery subsectors
- Fish Culture (culture fishery) – the act of raising the maximum productivity of fish or other edible aquatic products to satisfy human needs. This subsector is generally known as aquaculture.
- Fish Capture (capture fishery or fishing) – the act of catching or harvesting fish with the help of fishing gear like fishing hooks, pots, nets, etc. This refers to the fishing sub-sector
- Fish Preservation – a branch of fishery that deals with the scientific method of preserving fish and other edible aquatic products to prevent spoilage. These set of preservation techniques birthed the forth sub-sector of fishery: fish preservation.
The above branches are the three most popular branches of fishery. However, fish-related subsectors have increased over the years to yield three more major fishery subsectors: .
Origin of fish processing:
Fish is a highly perishable product! 😥 You will bear with me that when the catch becomes more than the fishers can preserve or conserve, they will have no choice but to process the excess fish into more useful derived and by-products, to be used by other agriculture sub-sectors. This branch deals with the processing of fish and other aquatic products and is popularly known as fish processing.
Origin of fishmongering:
It is generally agreed that small-scale subsistence fishery industries may just focus on satisfying the nutritional needs of the fisher. When it comes to large-scale industrial fisheries the scope becomes wider. These fish and their processed products are not just for the fishers or fish farmers alone. They are placed on both local and international markets to meet the needs of more people.
This is where another set of stakeholders, the fish sellers and buyers, come into the fishery chain. They, together with their commercial fishery activities, have yielded over the years, what is called: fishmongering. Now, the goal of fishmongering is not to culture, or to capture, or to preserve, or process, but to ensure that these protein-rich resources reach the targeted consumers worldwide.
Origin of fisheries management:
It came a point in time where fishing technology advanced such that the fisheries resources began to become exhausted. Then fisheries scienticed starting looking for techniques and government policies to ensure sustainable fishing. These set of management strategies with a view to sustain fish stocks is termed fishery management. To ensure sustainable capture fisheries, it has to be managed properly. A new subsector was birthed: fisheries management.
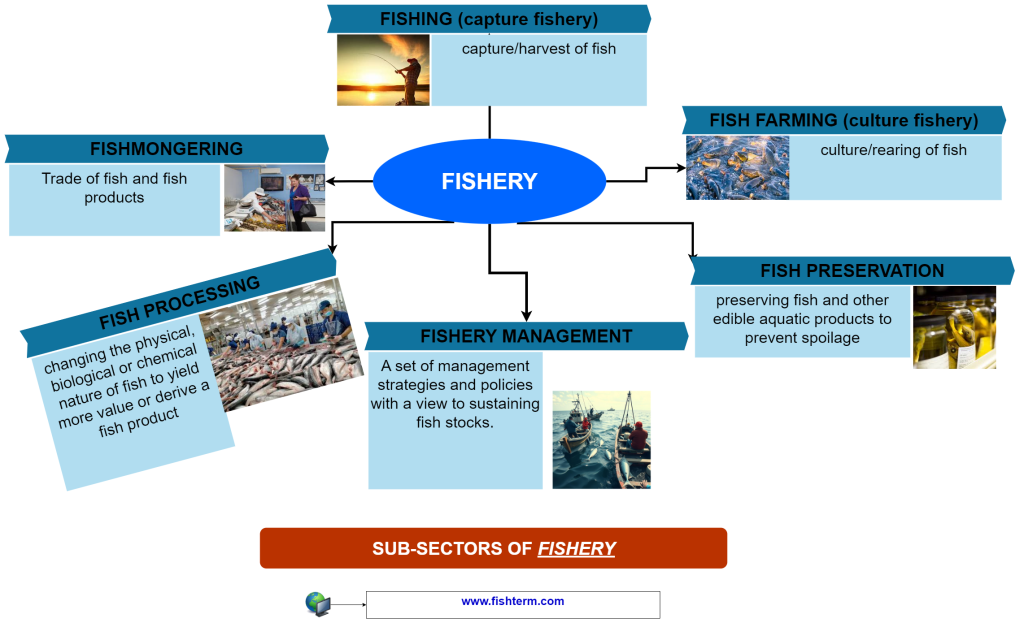
So, if we add up the three emerging sub-sectors to the 3 aforementioned popular ones, we can rewrite these sub-sectors of fishery into 6 main sub-sectors. These include:
- Aquaculture: culture of fish and other aquatic organisms;
- Fishing: catching or harvesting fish and other aquatic organisms;
- Fish Preservation: preserving fish and other edible aquatic products to prevent spoilage;
- Fish processing: changing the physical, biological or chemical nature of fish and other edible aquatic products to yield more value or derive a fish product;
- Fishmongering: trade of fish and the products thereof;
- Fishery management: set of management strategies and policies with a view to sustain fish stocks.
Explaining the 6 major sub-sectors and branches of fishery
1. Fish farming

Fish farming, also known as fish culture or pisciculture, is one of the major branches of fishery that raises to the productivity of edible aquatic products to satisfy human needs, by creating an environment with physico-chemical parameters similar to that of the cultured species’ natural environment. It is the second most popular and fastest branch of fisheries, after fishing. Fish farming is subdivided into many sub-sectors and types, classified holistically in ➡ this article on the branches of fish farming.
Some people consider fish farming to be synonymous with aquaculture. However, this was true in the past when aquaculture only meant fish cultivation. As time passed, the scope of aquaculture slowly broadened to mean the culture of fish and aquatic plants. Aquatic plants include algae like spirulina and seaweed.
Also known as aquafarming, or halieuculture, aquaculture is defined as: controlled cultivation (breeding or farming, raising, and harvesting) of aquatic organisms such as fish, shellfish, crustaceans, molluscs, algae and other valuable organisms such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus, seaweeds) in fresh, brackish or seawater. It involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions.
There is still a debate on whether aquatic plants should be considered fishes, and many fish specialists are against the idea. Since fish farming strictly means the cultivation of fish, and aquaculture nowadays doesn’t only cultivate fish, aquaculture is no longer a synonym for fish farming in many countries across the globe. Rather, fish farming is considered a branch under aquaculture, and aquaculture is considered a separate sector from fisheries – though they share some similarities.
Aquaculture is subdivided into many types, classified holistically in ➡ this article on the branches of aquaculture.
2. Fishing

Also called captured fishery, is one of the major branches of fishery dealing with catching or harvesting fish from a natural water body using fishing gear like fishing hooks, pots, nets, etc. It is also known as capture fishery.
Please read this article on our dictionary portal for holistic knowledge about fishing.
3. Fish Preservation
Fish preservation is one of the main branches of fishery that deals with the scientific methods used in preserving fish and other edible aquatic products to prevent spoilage. Some of these methods include salting, smoking, sun-drying, icing, etc.
Fish preservation originated far before the 1980’s as an activity. One of the earliest books published on this subject is Fish Preservation and Refrigeration by J. K. Kilbourn , published in 1883, under the International Fisheries Exhibition, London 1883.
Some methods of fish processing include:
- Ikejime method of fish slaughter;
- control of temperature using ice, refrigeration or freezing;
- chemical control of microbial loads by adding acids;
- oxygen deprivation, such as vacuum packing;
- control of water activity by drying, salting, smoking or freeze-drying;
- Physical control of microbial loads is done through microwave heating or ionising irradiation.
We have an article that covers fish preservation deeply. →Read more about fish processing on our Term portal
4. Fish processing

One of the branches of fishery that deals with changing the physical, biological or chemical nature of fish and other edible aquatic products to yield more value.
Fish processing means all processes associated with live or dead fish or fish products between the time fish are caught or harvested, and the time the final product is delivered to the customer. These involve fish preparation (fish is cleaned, part cleaned, scaled or cut up), fish decoration (fish marking, tagging, etc.), fish preservation (chilling, icing, freezing, irradiating, smoking, salting, cooking, etc.), and fish packaging (fish canning, bottling, or wrapping). Read more about fish processing on our Term portal.
The term ‘fish processing’ originated somewhere in the twentieth century, precisely before 1940 (confer the chart above). The term gained more popularity as years went by, right up to around the 1980’s, when the term ‘fish processing’ started declining in frequency, probably due to it being replaced with new synonyms like ‘seafood processing’.
However, we consider seafood processing to be a broader concept than fish processing, meaning not just the processing of fish but goes further to include all seafood in general (crabs, etc.).
The fish processing sector can be subdivided into other subsectors of fishery based on some criteria.
A. Based on the changes the raw fish undergoes after their capture, fish processing is subdivided into:
- Fish handling: preliminary processing of raw fish;
- Manufacture of fish products.
B. Based on the level in the processing chain the raw fish undergoes after their capture, fish processing is subdivided into:
- primary fish processing: involved in the filleting and freezing of fresh fish for onward distribution to fresh fish retail and catering outlets;
- secondary fish processing: which produces chilled, frozen and canned products for the retailers and caterers.
Fish processing is a plethora of activities like scaling, gilling, gutting, filleting, freezing, chilling, packing and
any other activity involved in preparing fish for sale.
We have an article that covers fish processing holistically. →Read more about fish processing on our Term portal
5. Fishmongering
Fishmongering is one of the main branches of fishery that deals with the trade of fish and their products. Stakeholders of this sector are called fishmongers. Fishmongers can be wholesalers or retailers and are trained at selecting and purchasing, boning, filleting, displaying, handling, gutting, merchandising and selling their products. A female fishmonger is known as a fishwife, fish-fag or fishlass.
The earliest known use of the noun fishmongering is in the 1810s. OED’s earliest evidence for fishmongering is from 1818, in British Monitor.
Leave a Reply